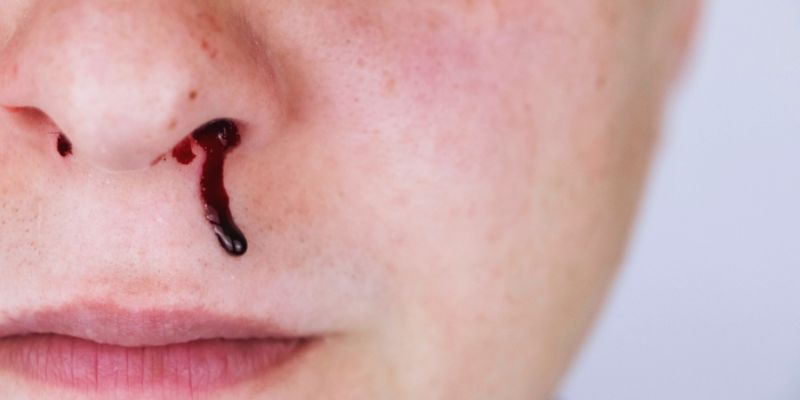
Understanding the Common Causes of Nosebleeds: What You Need To Know
A nosebleed or epistaxis occurs when a blood vessel in the nose's lining breaks. It can be triggered by various factors, including dry air, high blood pressure, injury, infection, nose pickling, allergic reaction, or an object hitting and pushing the nostrils. Nosebleeds are most common in children as they have small and delicate blood vessels in their noses that break easily.
However, the good part is that most nosebleeds can be treated at home and healed within 5 to 10 minutes. Also, they don't cause serious blood loss in kids or adults. But, if you cannot control the bleeding or suffer from frequent nosebleeds, you must consult a doctor. If you want to know more about nosebleeds and their major causes, stay here till the end and learn what you want to know about!

What Are The Causes Of Nosebleeds?
The lining of the nose is coated with mucosa, a humid, sensitive layer with many blood vessels near its exterior. The small wounds to this tissue can cause significant bleeding. Most nosebleeds damage only one nostril but can also affect both simultaneously. A nosebleed can be caused because of various reasons, including:
A Dry Climate Or Home Environment
Dry air is the most prevalent reason for nosebleeds. A dry atmosphere or warm environment in homes hurts and dries up nose membranes, which may break the soft skin within the nose and cause bleeding. Nosebleeds are more prone to pop up when weather conditions vary and the nasal tissues have not adjusted to the increasing or decreasing moisture content. Nosebleeds are most challenging in the winter when the climate becomes extremely cold and dry. The climate within our homes exacerbates this dryness. For instance, the majority of the homes have heating systems to keep the homes warm. This type of heat causes the air to dry and removes the moisture from the environment. To avoid nosebleeds, it becomes crucial to keep a humidity device in the house to increase the moisture level gradually. Besides that, staying hydrated is also crucial, making your body's cells fresh and healthy. Also, you can use the saline nasal spray to moisten your nose and avoid pushing things in the nose.
Allergies
The common flu, fever, and other breathing-related diseases can cause a boost in mucus and excessive nose-blowing and sneezing. Allergic responses are similar to it. They may harm the soft tissue of the nose, increasing the chance of bleeding. Allergic patients use nasal sprays, which might exacerbate their symptoms. Putting the nasal spray nozzle into the nostrils may damage the nose's interior. If the substance is not properly spread when sprayed, it can build up in the tip of the nose, bringing irritation. People with excessively high blood pressure or a biological disorder such as hemorrhagic telangiectasia are more prone to bleeding.
Nose Picking
When the nose gets rubbed or beaten up, its tiny blood veins can rupture. Thus, infants who pick their noses or push things into their nostrils are at greater risk of experiencing nosebleeds. Picking your nose doesn't kill you; however, it is a dangerous habit and may contribute to a nasal passage problem. Picking up a dry nose may reduce pain and cause additional discomfort, bleeding, scratching, or swelling. It can also spread bacteria. But the good part is that you can prevent nosebleeds by using your thumb to rub the soft sides of the nose when needed.
Nasal Trauma
Nasal trauma is the most prevalent factor behind nosebleeding. It indicates damage to your nose or the tissues that protect and sustain it. Because of its position, your nose's bones, cartilage, and tissues are more prone to outside trauma. Many of your nose's blood arteries are close to the outermost layer, so even minor nasal damage frequently leads to nosebleeds. The bleeding goes away if you use the proper procedure. If the bleeding continues, consult with a doctor. Nasal trauma symptoms may differ from moderate to severe based on the nature and severity of the injury. Causes of nasal trauma include sports injuries, abuse, accidents, nasal piercing infections, and clogging of something in the nose.

Bleeding Disorder
Bleeding disorders lead to nosebleeds because they weaken the body's ability to build clots. Bleeding problems may be hereditary or induced. HHT (Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia), for example, is a genetic condition that causes abnormal blood vessel creation, resulting in major or deadly bleeding. Persistent nosebleeds are the most typical symptom. Someone with HHT (Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia) may have unusual capillaries or vascular links between blood vessels and arteries. Capillaries are small channels carrying blood from the blood vessels to the veins. The strange blood vessels generated in HHT can become weak and may break down, resulting in bleeding. Other blood illnesses include anemia, hemophilia, blood clots, and blood tumors like leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma.
Medications
Certain medicines affect the blood's capacity to clump together. Prescription blood thinners and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines like aspirin and ibuprofen fall under this category. Using any of these medicines may increase the chance of nosebleeds. Some nasal sprays, particularly those carrying steroids for managing allergies, might cause nosebleeds. When using a nasal spray, strictly follow the instructions to reduce the possibility of nosebleeds and other complications. Substances included in some homeopathic medicines and food additives cause bleeding to last longer.
Conclusion:
Nosebleeds are widespread and sometimes can be harmful. The majority are anterior nosebleeds, which are usually manageable at home. They frequently appear unexpectedly and do not remain longer. The tissues in the nose are sensitive and easily get injured. This type of injury is typically caused by pinching one's nose or breathing dry air. Having your home's air moist, minimizing nose picking, and utilizing nasal sprays to keep your passageways wet can help prevent nosebleeds. If you are unable to stop the bleeding from an anterior nosebleed, contact your doctor urgently before it gets too late!